Medicine is often a field at the forefront of technology. The importance of the field itself combined with the lucrative payouts seen for successful medical devices attracts many entrepreneurs and companies to the field. One of the most intriguing new technological advances is Google Glass – the augmented-reality glasses developed by tech powerhouse Google. There has been much speculation about the use of Google Glass in medicine. The possible implementation of Google Glass within the medical field raises important questions about how Google Glass may change medical education and practice.
What is Google Glass?
Google Glass is an augmented-reality system developed by Google. It is a voice-controlled, hands-free computing system that is housed in a “glasses” interface that users can wear much like spectacles. It contains an HD capable screen, 5 megapixel camera, and is Bluetooth, WiFi, and GPS enabled. The interface can sync with both Android and iOS phones for integration of information across platforms. Google Glass is currently in its “Explorer” beta phase, with a retail price of $1500. Speculation is that the upcoming retail version will be greatly reduced in cost.
What are the uses for Google Glass in Medicine?
The combination of features present in the Glass package makes it an enticing future medical tool. The main hypothesized role for Glass is in information sharing and transfer. Glass may prove useful in allowing physicians access to patient medical records, imaging studies, and pharmaceutical information in real time via the integrated HD screen. Glass may also be useful for physicians on home-call, as information about patient’s vitals and status can be relayed while the physician is en-route to the care facility. In the surgical field, Glass may help with surgical procedures by providing instant access to reference materials and real-time consults in the operating room. Finally, Glass may provide a more integrated and unique experience for medical students. Students will be able to view patient interactions and procedures with the same point of view (POV) as the physician, providing an unparalleled immersive educational experience. Furthermore, use of Glass by patients will allow students to view patient encounters from the patient’s POV, providing a perspective that many students may never have otherwise experienced.

How is Google Glass Currently Being Used?
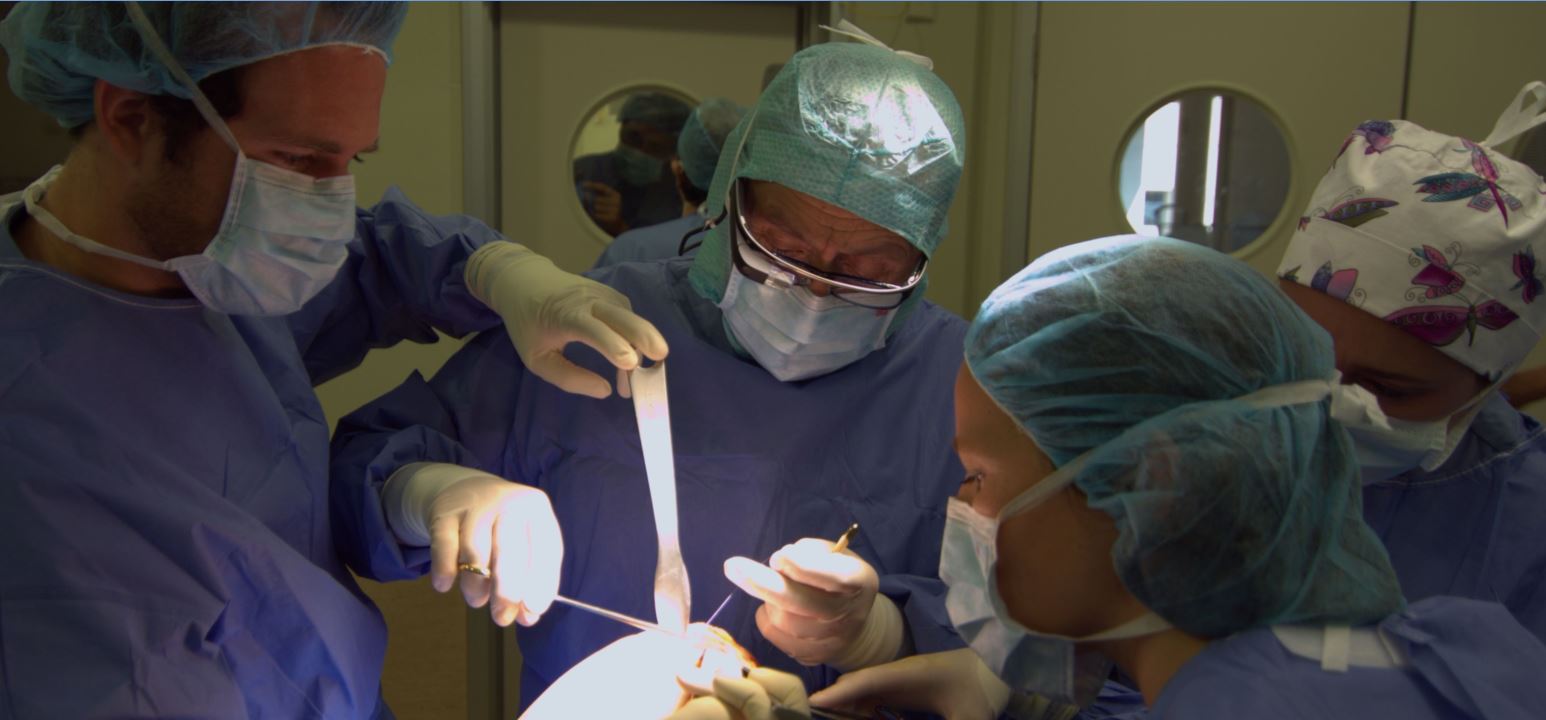
While Google Glass is still in its infant stages, there has been some limited implementation in the medical field. Dr. Christopher Kaeding, an orthopedic surgeon at the Ohio State University, was the first physician to use Glass during a surgical procedure. The procedure was broadcast via Glass to both medical students and faculty at the university.
In terms of education, the University of California – Irvine Medical School has implemented Glass in its innovative iMedEd program. Established in 2010, iMedEd provides medical students at UC Irvine with specialized technological access and training. It started with school-issued iPads for every medical student, and later expanded to point-of-care ultrasound training and use. In 2014, the iMedEd program began utilizing 10 pairs of Glass to be distributed amongst the 3rd and 4th year medical students on the wards. It will be an interesting development to see how Glass is received amongst the students, and how they rate its effectiveness at enriching their educational experience.
What needs to happen for Glass to have widespread adoption in the medical field?
While Glass does have intriguing possibilities, it is by no means a proven entity in the medical field. I believe that for Glass to become an influential medical product two things have to happen. The first thing that must happen is that Glass must be utilized extensively in the consumer market. Many of the questions about Glass revolve around public uncertainty about privacy issues. If Glass gains a large foothold in the consumer marker, patients will become accustomed to interacting with Glass users and will feel less hesitant in a Glass-using setting. The second thing that must happen is that app developers must create useful medical apps for Glass. These apps must both provide utility to physicians and be compliant with HIPAA regulations. Much like EPIC was to electronic medical records, Glass needs companies who are willing to take on the intense regulatory scrutiny of the medical field in app development.
Sources:
- http://mhadegree.org/will-google-glass-revolutionize-the-medical-industry/
- http://news.uci.edu/press-releases/uci-school-of-medicine-first-to-integrate-google-glass-into-curriculum/
- http://osuwmc.multimedianewsroom.tv/story.php?id=663
Featured image:
Google Glass Dr. Guillen


4 replies on “Medical Technology: Google Glass and the Future of Medical Education and Practice”
Hello, great information and an fascinating article, it’s going to be interesting if this is still the case in a few months time
Wonderful Piece
Hi, great suggestion and an fascinating post, it is going to
be fascinating if this is still the case in a few years time
This is great thing that even big giants are trying to make things which can be helpful in health care industry..!!